Using KPI In Measuring Marketing ROI

Return on investment (ROI) is a crucial metric in marketing used to gauge the profitability and effectiveness of marketing campaigns and activities. It measures the financial return generated by marketing expenditures relative to their initial cost, providing insights into how much money is made or lost as a result of these activities.
In marketing, ROI is determined using the following formula:
ROI is calculated as (Net Profit from Marketing Campaign / Campaign Cost) x 100.
Generally, a percentage is used to indicate the outcome. A positive ROI indicates that the marketing campaign generated more revenue than it cost, while a negative ROI means the campaign incurred a loss.
Why ROI Metrics Are Important in Marketing Campaign
Measuring ROI offers several significant benefits, including providing a transparent and unbiased view of a campaign's performance. This shifts marketers from relying on gut feelings to using hard evidence of achievements or areas needing improvement. It enhances accountability within marketing teams and strengthens the alignment between marketing initiatives and overall business goals.
Furthermore, ROI measurement helps businesses identify the most effective marketing programs, content, and channels. By understanding which technique deliver the highest returns, marketers can focus on efforts that add real value, increasing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of promotional activities.
-
Evaluating Customer Value
Assessing the ROI of marketing programs is essential for evaluating customer value. By tracking customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, and repeat purchase rates, companies can determine the real benefits their marketing efforts bring to their clientele. This fosters strong, lasting customer relationships, enhancing customer retention and loyalty.
-
Optimizing Budget Allocation
ROI measurement is critical for budget allocation, ensuring that marketing funds are directed towards the most profitable avenues. It helps identify underperforming campaigns and channels, enabling timely adjustments and reducing unnecessary expenditures. This financial discipline helps companies maintain a competitive edge and overall cost-effectiveness.
-
Encouraging Innovation and Continuous Improvement
ROI assessment encourages marketing teams to innovate and continually improve. With insights into what works best, marketers can experiment with new ideas, explore creative approaches, and continually refine their strategies based on real-time data. This iterative optimization process keeps marketing efforts relevant and promotes sustained growth and success in a constantly evolving market.
.jpg)
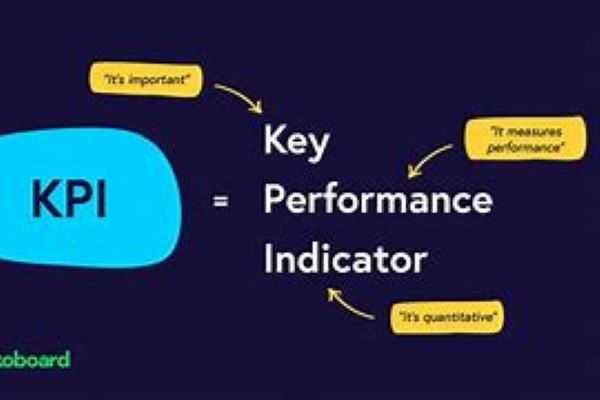
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Determining Marketing ROI
KPIs are quantifiable measurements that show how well you're doing at achieving your marketing objectives over a given time frame. Below are the KPI metrics used in determining Marketing ROI:
1. Sales Revenue
Sales revenue is one of the most basic measures for calculating marketing ROI. It represents the total revenue directly generated by a marketing campaign or activity. Linking specific sales to a particular campaign allows businesses to gauge the direct impact of their marketing expenditures on revenue generation.
2. Cost per Acquisition (CPA)
CPA measures the average cost of acquiring a new customer through a marketing campaign. It is calculated by dividing the total campaign expenditure by the number of new customers acquired. A lower CPA indicates that the marketing campaign is effectively attracting new customers at a lower cost, boosting ROI.
3. Conversion Rate
The conversion rate is the percentage of potential customers or website visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, subscribing to a newsletter, or filling out a form. A high conversion rate signifies that the marketing efforts are successfully engaging and persuading prospects, leading to a higher ROI.
4. Customer Retention Rate
This metric indicates the percentage of existing customers who are retained over a specific period. It is a crucial indicator of the effectiveness of marketing campaigns in fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty. A higher retention rate leads to increased customer lifetime value and a higher overall ROI.
5. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
CLV represents the total value a customer is expected to bring to a business over their lifetime. Understanding the long-term revenue potential from customers allows marketers to evaluate the ROI of acquiring and retaining customers. A higher CLV justifies higher acquisition costs and indicates a better return on marketing investment.
6. Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS)
One indicator that is very relevant to advertising campaigns is ROAS. It calculates the amount of money made for every dollar spent on advertising. The equation is:
Revenue from Advertising / Expense of Advertising Campaign = ROAS
A campaign that yielded a positive return on investment (ROI) is one where revenue exceeded advertising costs (ROAS value greater than 1).

Defining Purposes and Objectives for Marketing ROI
Establishing clear goals and objectives is vital for accurately calculating marketing ROI. Without well-defined objectives, it becomes challenging to assess the effectiveness of marketing efforts and their impact on overall business performance.
Here’s how to set precise objectives and goals for determining marketing ROI:
1. Be Specific
Clearly articulate the goal and desired outcomes of the marketing strategy. This could include increasing sales, enhancing brand awareness, generating leads, boosting website traffic, or improving customer retention.
2. Define Measurable Indicators
Ensure the objectives are measurable and tangible. Use KPIs such as sales revenue, click-through rates, conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, or customer lifetime value, depending on the campaign’s goals.
3. Set Targets
Establish specific numerical targets for each objective. For example, aim for a 20% increase in website traffic, a 5% conversion rate, or a 10% reduction in customer acquisition costs.
4. Set Deadlines
Determine the timeline for achieving the goals. This could be during the duration of a specific campaign or over a predetermined period, such as quarterly or annually.
By understanding and applying these principles, businesses can effectively measure and enhance the ROI of their marketing campaigns, ensuring that their efforts are both profitable and aligned with their overall strategic goals.
Author Bio
Contributor comprises full-time and freelance writers that form an integral part of the Editorial team of Hubslides working on different stages of content writing and publishing with overall goals of enriching the readers' knowledge through research and publishing of quality content.
Article Comments
No Comments!
At present there are zero comments on this article.
Why not be the first to make a comment?
Similar Articles
Sponsor
Search Articles
Experts Column
Latest Articles
Featured Articles
Most Popular Articles












