Easy Ways To Recognize Which Vitamins Are Fat Soluble and Water Soluble
Vitamins are nutrients found in food that aid in the proper functioning of the human body but which vitamins are fat soluble?
Types of Vitamins
There are two types of vitamins:
Vitamins that are water-soluble, such as vitamins B and C, dissolve in water.
Fat-soluble vitamins dissolve in fat. This type of vitamins such as A, D, E, and K, are best absorbed by the body when eaten with high-fat foods.

During digestion, both fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins are absorbed. Excess fat-soluble vitamins are then stored in the liver and fatty tissues, while excess water-soluble vitamins are flushed out.
Vitamins that are fat-soluble enter the bloodstream through lymph channels in the intestinal wall. Proteins transport many fat-soluble vitamins throughout the body.
Fat-soluble vitamins absorption
To be more specific, fat-soluble vitamins travel through the body in the following order and pathway:
Vitamins are absorbed through the food we eat. The food is partially digested in the stomach before being transferred to the small intestine for further digestion.
Bile is required for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. The bile then travels to the small intestine, where it begins to break down fats.
Vitamins are then absorbed through the wall of the intestine. The fat-soluble vitamin is absorbed into the lymph vessels and then into the bloodstream.
Normally, a protein is required to transport a fat-soluble vitamin throughout the body. Excess vitamins are stored in the fatty tissue and liver of the body.
When the body requires a vitamin, it draws from its reserves. The vitamin is released from the liver into the bloodstream.
Other than the food, fat-soluble vitamins can be obtained from other sources. When the skin is exposed to the sun, vitamin D is produced naturally by the body.
Vitamin supplements can also be used to help people meet their daily requirements. But which foods have the highest concentrations of fat-soluble vitamins?
Vitamins that are fat-soluble
Vitamins that dissolve in fats (lipids) are known as fat-soluble vitamins.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A serves a variety of functions in the body. It aids the immune system in the fight against infections. It's essential for glowing skin, clear vision, and healthy intestines.
Vitamin A deficiency can lead to night blindness, skin disorders, and an increased risk of infection. Low vitamin A levels have also been linked to zinc deficiency, which can stifle growth.
Vitamin A is found in animal foods like liver, eggs, and milk, as well as darkly coloured fruits and vegetables like the following:
- Carrots
- Sweet potatoes
- Cantaloupes
- Apricots
- Peaches
- Spinach
- Broccoli
.jpg)
Vitamin D
Vitamin D keeps the right amount of calcium and phosphorus in your blood, which helps you build and maintain strong bones and teeth. Bones can become thin and brittle if they don't get enough vitamin D.
Osteoporosis and osteopenia are common in people with cystic fibrosis. Vitamin D also aids in the proper functioning of the immune and nervous systems.
Vitamin D is produced in part by exposure to sunlight, but it is often insufficient. Many people with CF require additional vitamin D beyond what is provided in CF-specific multivitamins.
Vitamin D can also be found in the following foods:
- Sardines (salmon) Mackerel (mackerel)
- Cereal Eggs with Tuna Milk
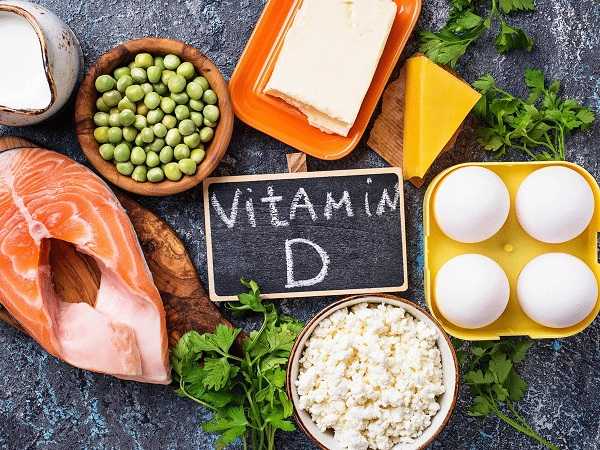

Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an antioxidant, which means it prevents the body's compounds from reacting with oxygen.
Compounds that have been oxidized become harmful to the body.
Vitamin E also aids in the formation of red blood cells and the maintenance of a healthy nervous and immune system.
It's difficult to get enough vitamin E from food alone. Small amounts can be found in some fruits and vegetables.
It is absent from the majority of meat products. Vitamin E supplements and the foods listed below are good sources:
- Peanuts
- Almonds
- Mayonnaise
- Bread (whole grain) with broccoli margarine
.jpg)
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is best known for its ability to aid in the formation of blood clots. A cut could bleed for a long time without it, and a small bruise could turn into a large bruise.
Vitamin K is also beneficial to bone health. Some of the vitamin K you need is made in your intestines, but people who take antibiotics may have less of it.
Vitamin K is included in all multivitamin supplements designed for people with CF, but not all over-the-counter multivitamins are.
If you're not taking CF-specific multivitamins, make sure to read the ingredient label and choose one that contains vitamin K.
Eat a lot of dark green, leafy vegetables to get enough vitamin K in your diet. Here are some vitamin K-rich foods:
- Broccoli
- Lettuce with spinach leaves
- Peas
- Brussels sprouts
- Salad dressing
- Kale
.jpg)
Vitamins that are fat-soluble are stored in the liver and fatty tissues.
When fat-soluble vitamins A and D are consumed in excess, they can build up and cause problems.
Fat-soluble vitamins are not destroyed by cooking.
Some conditions, known as malabsorption disorders, prevent fats and thus fat-soluble vitamins from being absorbed.
Mineral oil, for example, has a similar effect. Mineral oil dissolves fat-soluble vitamins, which the body does not absorb.
As a result, when people take mineral oil (for example, as a laxative), these vitamins are carried out of the body unabsorbed.
Author Bio
The Editorial staff includes content researchers from various areas of knowledge. They add a plethora of expertise to the Hubslides Editorial team. They constantly and frequently oversee, produce and evaluate contents that are most ideal to aid impacting knowledge to readers.
Article Comments
No Comments!
At present there are zero comments on this article.
Why not be the first to make a comment?
Similar Articles
Sponsor
Search Articles
Experts Column
Latest Articles
Featured Articles
Most Popular Articles












